Fixing alerts
Once a secret has been committed to a repository, you should consider the secret compromised. GitHub recommends the following actions for compromised secrets:
- Verify that the secret committed to GitHub is valid. See Performing an on-demand validity check.
- For secrets detected in private repositories, report the leaked secret to GitHub, who will treat it like any publicly leaked secret and revoke it. Applies to GitHub personal access tokens only. See Reporting a leaked secret.
- Review and update any services that use the old token. For GitHub personal access tokens, delete the compromised token and create a new token. See Managing your personal access tokens.
- Depending on the secret provider, check your security logs for any unauthorized activity.
Reporting a leaked secret
Note
Reporting a privately exposed secret to GitHub is in public preview and subject to change. The feature is currently only available for GitHub personal access tokens (v1 and v2).
If a secret is detected in a public repository on GitHub and the secret also matches a supported partner pattern, the potential secret is automatically reported to the service provider. For details of all supported partner patterns, see Supported secret scanning patterns.
For secrets detected in private repositories, anyone who can view secret scanning alerts for a repository can choose to report the privately exposed secret directly to GitHub.
By reporting the secret, the token provider will treat the privately exposed secret as if it had been publicly leaked. This means the token provider may revoke the secret, so you should first consider reviewing and updating any services that use the secret. If possible, you should also consider notifying the token owner before reporting the token, so that the token owner is aware that the secret may get revoked.
You will only see the option to report a privately exposed secret to GitHub if the following conditions are met:
- The secret is a GitHub personal access token.
- The secret's validity has not been confirmed, or the secret's validity has been confirmed as
active.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under the repository name, click Security. If you cannot see the "Security" tab, select the dropdown menu, and then click Security.
-
In the left sidebar, under "Vulnerability alerts", click Secret scanning.
-
From the alert list, click the alert you want to view.
-
In the alert view for the leaked secret, click Report leak.
Note
In order to prevent breaking workflows, consider first rotating the secret before continuing, as disclosing it could lead to the secret being revoked. If possible, you should also reach out to the token owner to let them know about the leak and coordinate a remediation plan.
-
Review the information in the dialog box, then click I understand the consequence, report this secret.
Closing alerts
Note
Secret scanning doesn't automatically close alerts when the corresponding token has been removed from the repository. You must manually close these alerts in the alert list on GitHub.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under the repository name, click Security. If you cannot see the "Security" tab, select the dropdown menu, and then click Security.

-
In the left sidebar, under "Vulnerability alerts", click Secret scanning.
-
Under "Secret scanning", click the alert you want to view.
-
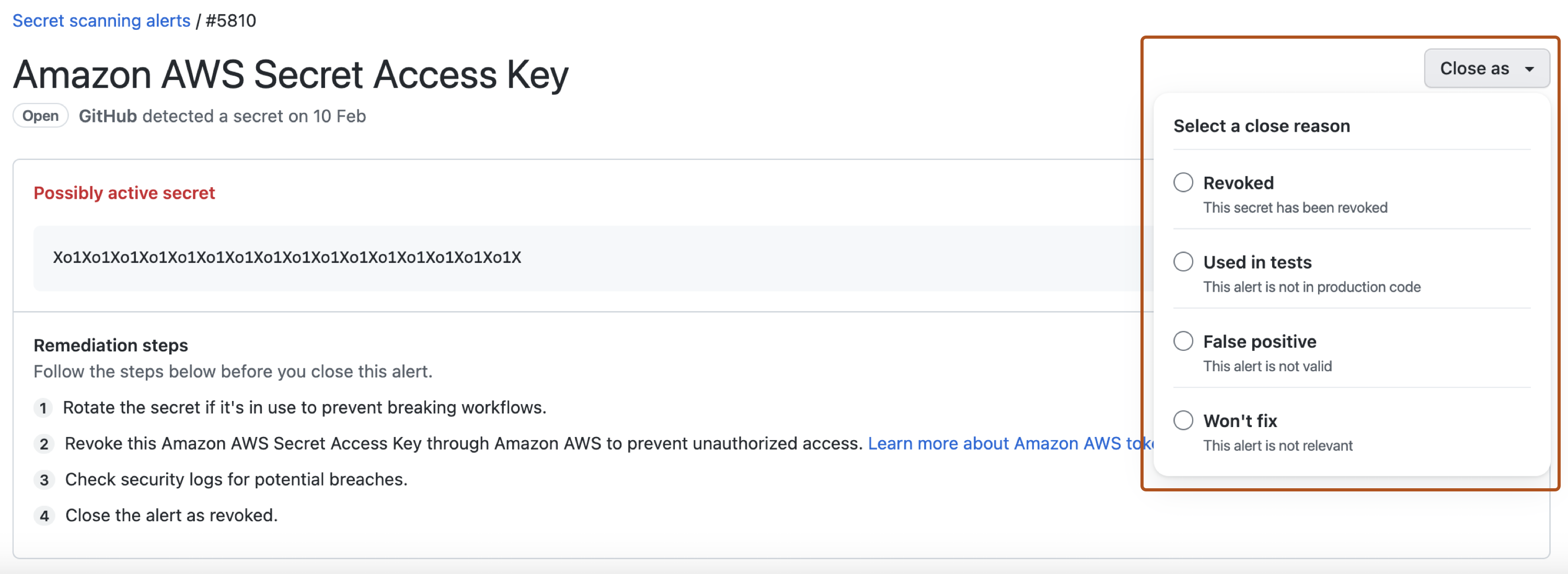
To dismiss an alert, select the "Close as" dropdown menu and click a reason for resolving an alert.
-
Optionally, in the "Comment" field, add a dismissal comment. The dismissal comment will be added to the alert timeline and can be used as justification during auditing and reporting. You can view the history of all dismissed alerts and dismissal comments in the alert timeline. You can also retrieve or set a comment by using the Secret scanning API. The comment is contained in the
resolution_commentfield. For more information, see REST API endpoints for secret scanning in the REST API documentation. -
Click Close alert.