About the secret scanning alerts page
When you enable secret scanning for a repository or push commits to a repository with secret scanning enabled, GitHub scans the contents for secrets that match patterns defined by service providers and any custom patterns defined in your enterprise, organization, or repository.
When secret scanning detects a secret, GitHub generates an alert. GitHub displays an alert in the Security tab of the repository.
To help you triage alerts more effectively, GitHub separates alerts into two lists:
- Default alerts
- Experimental alerts
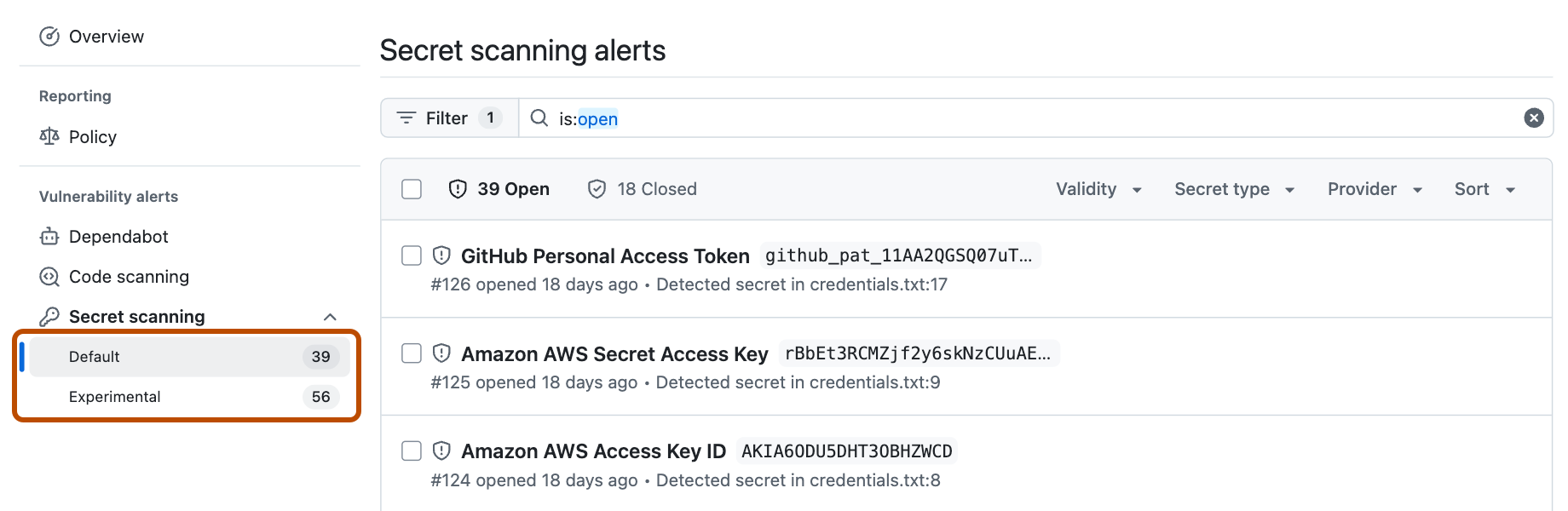
Default alerts list
The default alerts list displays alerts that relate to supported patterns and specified custom patterns. This is the main view for alerts.
Experimental alerts list
The experimental alerts list displays alerts that relate to non-provider patterns (such as private keys), or generic secrets detected using AI (such as passwords). These types of alerts can have a higher rate of false positives or secrets used in tests. You can toggle to the experimental alerts list from the default alerts list.
In addition, alerts that fall into this category:
- Are limited in quantity to 5000 alerts per repository (this includes open and closed alerts).
- Are not shown in the summary views for security overview, only in the "Secret scanning" view.
- Only have the first five detected locations shown on GitHub for non-provider patterns, and only the first detected location shown for AI-detected generic secrets.
For GitHub to scan for non-provider patterns and generic secrets, you must first enable the features for your repository or organization. For more information, see Enabling secret scanning for non-provider patterns and Enabling Copilot secret scanning's generic secret detection.
GitHub will continue to release new patterns and secret types to the experimental alerts list and will promote them to the default list when feature-complete (e.g. when they have an appropriately low volume and false positive rate).
Viewing alerts
Alerts for secret scanning are displayed under the Security tab of the repository.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under the repository name, click Security. If you cannot see the "Security" tab, select the dropdown menu, and then click Security.
-
In the left sidebar, under "Vulnerability alerts", click Secret scanning.
-
Optionally, toggle to "Experimental" to see alerts for non-provider patterns or generic secrets detected using AI.
-
Under "Secret scanning", click the alert you want to view.
Note
Only people with admin permissions to the repository containing a leaked secret can view security alert details and token metadata for an alert. Enterprise owners can request temporary access to the repository for this purpose.
Filtering alerts
You can apply various filters to the alerts list to help you find the alerts you're interested in. You can use the dropdown menus above the alerts list, or input the qualifiers listed in the table into the search bar.
| Qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
is:open | Displays open alerts. |
is:closed | Displays closed alerts. |
is:publicly-leaked | Displays alerts for secrets that have been found in a public repository. |
is:multi-repository | Displays alerts for secrets that have been found in more than one repository within the same organization or enterprise. |
bypassed: true | Displays alerts for secrets where push protection has been bypassed. For more information, see About push protection. |
validity:active | Displays alerts for secrets that are known to be active. For more information about validity statuses, see Evaluating alerts from secret scanning. |
validity:inactive | Displays alerts for secrets that are no longer active. |
validity:unknown | Displays alerts for secrets where the validity status of the secret is unknown. |
secret-type:SECRET-NAME | Displays alerts for a specific secret type, for example, secret-type:github_personal_access_token. For a list of supported secret types, see Supported secret scanning patterns. |
provider:PROVIDER-NAME | Displays alerts for a specific provider, for example, provider:github. For a list of supported partners, see Supported secret scanning patterns. |
results:default | Displays alerts for supported secrets and custom patterns. For a list of supported patterns, see Supported secret scanning patterns. |
results:experimental | Displays alerts for non-provider patterns, such as private keys, and AI-detected generic secrets, such as passwords. For a list of supported non-provider patterns, see Supported secret scanning patterns. For more information about AI-detected generic secrets, see Responsible detection of generic secrets with Copilot secret scanning. |