참고: GitHub 호스트 실행기는 현재 GitHub Enterprise Server에서 지원되지 않습니다. GitHub public roadmap에 예정된 향후 지원에 대해 자세히 알아볼 수 있습니다.
예제 개요
이 문서에서는 예제 워크플로를 사용하여 GitHub Actions의 주요 CI 기능 중 일부를 보여 줍니다. 이 워크플로가 트리거되면 npm test와의 테스트 조합 매트릭스를 사용하여 코드를 테스트합니다.
다음 다이어그램에서는 워크플로의 단계와 작업 내에서 실행되는 방법에 대한 개략적인 보기를 보여 줍니다.
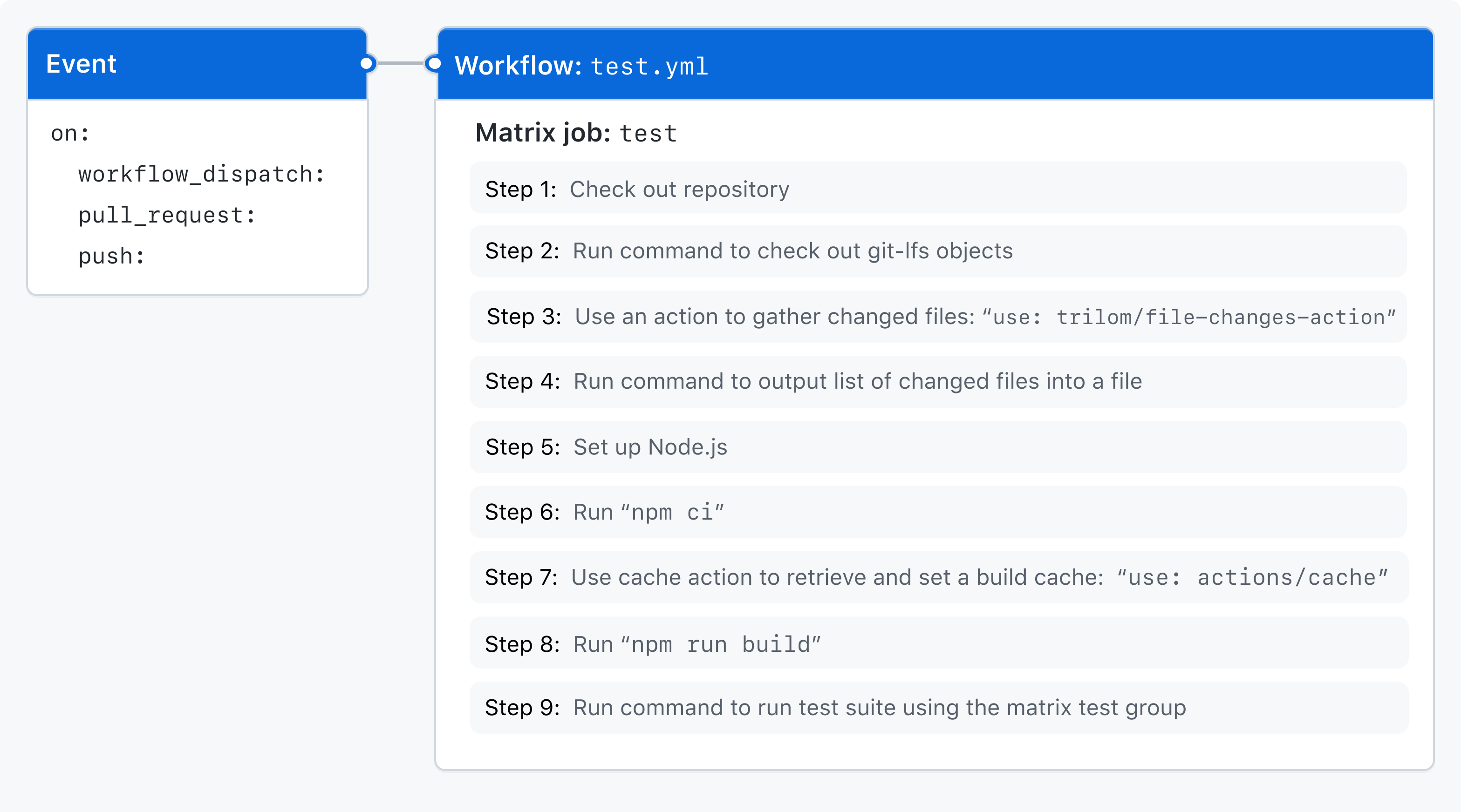
이 예제에서 사용되는 기능
예제 워크플로는 GitHub Actions의 다음 기능을 보여 줍니다.
| 기능 | 구현 |
|---|---|
| UI에서 워크플로 수동 실행 | workflow_dispatch |
| 워크플로 자동 실행 트리거: | pull_request |
| 정기적으로 워크플로 실행 | schedule |
| 토큰에 대한 사용 권한 설정 | permissions |
| 동시에 실행할 수 있는 워크플로 실행 또는 작업 수 제어 | concurrency |
| 리포지토리에 따라 다른 실행기에 작업 실행 | runs-on |
| 매트릭스를 사용하여 다른 테스트 구성 만들기 | matrix |
실행기에 node 설치 | actions/setup-node |
| 종속성 캐싱 | actions/cache |
| 실행기에서 테스트 실행 | npm test |
예시 워크플로
다음 워크플로는 GitHub Docs Engineering 팀에서 만들었습니다. 워크플로는 끌어오기 요청의 코드에 대한 테스트를 실행합니다. github/docs 리포지토리에서 이 파일의 최신 버전을 검토하려면 test.yml을 참조하세요.
# 이렇게 하면 GitHub 리포지토리의 "작업" 탭에 표시되는 워크플로의 이름이 정의됩니다.
name: Node.js Tests
# The `on` keyword lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/triggering-a-workflow#using-events-to-trigger-workflows)."
on:
# Add the `workflow_dispatch` event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow. For more information, see [`workflow_dispatch`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_dispatch).
workflow_dispatch:
# Add the `pull_request` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see [`pull_request`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#pull_request).
pull_request:
# Add the `push` event with the `branch` filter, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called "main". For more information, see [`push`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#push).
push:
branches:
- main
# This modifies the default permissions granted to `GITHUB_TOKEN`. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/assigning-permissions-to-jobs)."
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: read
# The `concurrency` key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/using-concurrency)."
# `concurrency.group` generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The `||` operator is used to define fallback values.
# `concurrency.cancel-in-progress` cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: true
# This groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
jobs:
# This defines a job with the ID `test` that is stored within the `jobs` key.
test:
# This configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
#
# In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named `docs-internal` and is within the `github` organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an `ubuntu-latest` runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/choosing-the-runner-for-a-job)."
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}
# This sets the maximum number of minutes to let the job run before it is automatically canceled. For more information, see [`timeout-minutes`](/actions/using-workflows/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#jobsjob_idtimeout-minutes).
timeout-minutes: 60
# This section defines the build matrix for your jobs.
strategy:
# Setting `fail-fast` to `false` prevents GitHub from cancelling all in-progress jobs if any matrix job fails.
fail-fast: false
# This creates a matrix named `test-group`, with an array of test groups. These values match the names of test groups that will be run by `npm test`.
matrix:
test-group:
[
content,
graphql,
meta,
rendering,
routing,
unit,
linting,
translations,
]
# This groups together all the steps that will run as part of the `test` job. Each job in a workflow has its own `steps` section.
steps:
# The `uses` keyword tells the job to retrieve the action named `actions/checkout`. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use your repository's code. Some extra options are provided to the action using the `with` key.
- name: Check out repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
lfs: ${{ matrix.test-group == 'content' }}
persist-credentials: 'false'
# This step runs a command to check out large file storage (LFS) objects from the repository.
- name: Checkout LFS objects
run: git lfs checkout
# This step uses the `trilom/file-changes-action` action to gather the files changed in the pull request, so they can be analyzed in the next step. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the `a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b` SHA.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
id: get_diff_files
with:
output: ' '
# This step runs a shell command that uses an output from the previous step to create a file containing the list of files changed in the pull request.
- name: Insight into changed files
run: |
echo "${{ steps.get_diff_files.outputs.files }}" > get_diff_files.txt
# This step uses the `actions/setup-node` action to install the specified version of the `node` software package on the runner, which gives you access to the `npm` command.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.14.x
cache: npm
# This step runs the `npm ci` shell command to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
# This step uses the `actions/cache` action to cache the Next.js build, so that the workflow will attempt to retrieve a cache of the build, and not rebuild it from scratch every time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/caching-dependencies-to-speed-up-workflows)."
- name: Cache nextjs build
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: .next/cache
key: ${{ runner.os }}-nextjs-${{ hashFiles('package*.json') }}
# This step runs the build script.
- name: Run build script
run: npm run build
# This step runs the tests using `npm test`, and the test matrix provides a different value for `${{ matrix.test-group }}` for each job in the matrix. It uses the `DIFF_FILE` environment variable to know which files have changed, and uses the `CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH` environment variable for the changelog cache file.
- name: Run tests
env:
DIFF_FILE: get_diff_files.txt
CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH: src/fixtures/fixtures/changelog-feed.json
run: npm test -- tests/${{ matrix.test-group }}/
name: Node.js Tests이렇게 하면 GitHub 리포지토리의 "작업" 탭에 표시되는 워크플로의 이름이 정의됩니다.
on:The on keyword lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "워크플로 트리거."
workflow_dispatch:Add the workflow_dispatch event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow. For more information, see workflow_dispatch.
pull_request:Add the pull_request event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see pull_request.
push:
branches:
- mainAdd the push event with the branch filter, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called "main". For more information, see push.
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: readThis modifies the default permissions granted to GITHUB_TOKEN. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "작업에 권한 할당."
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: trueThe concurrency key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "동시성 사용."
concurrency.group generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The || operator is used to define fallback values.
concurrency.cancel-in-progress cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
jobs:This groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
test:This defines a job with the ID test that is stored within the jobs key.
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}This configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named docs-internal and is within the github organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an ubuntu-latest runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "작업에 대한 실행기 선택."
timeout-minutes: 60This sets the maximum number of minutes to let the job run before it is automatically canceled. For more information, see timeout-minutes.
strategy:This section defines the build matrix for your jobs.
fail-fast: falseSetting fail-fast to false prevents GitHub from cancelling all in-progress jobs if any matrix job fails.
matrix:
test-group:
[
content,
graphql,
meta,
rendering,
routing,
unit,
linting,
translations,
]This creates a matrix named test-group, with an array of test groups. These values match the names of test groups that will be run by npm test.
steps:This groups together all the steps that will run as part of the test job. Each job in a workflow has its own steps section.
- name: Check out repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
lfs: ${{ matrix.test-group == 'content' }}
persist-credentials: 'false'The uses keyword tells the job to retrieve the action named actions/checkout. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use your repository's code. Some extra options are provided to the action using the with key.
- name: Checkout LFS objects
run: git lfs checkoutThis step runs a command to check out large file storage (LFS) objects from the repository.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
id: get_diff_files
with:
output: ' 'This step uses the trilom/file-changes-action action to gather the files changed in the pull request, so they can be analyzed in the next step. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b SHA.
- name: Insight into changed files
run: |
echo "${{ steps.get_diff_files.outputs.files }}" > get_diff_files.txtThis step runs a shell command that uses an output from the previous step to create a file containing the list of files changed in the pull request.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.14.x
cache: npmThis step uses the actions/setup-node action to install the specified version of the node software package on the runner, which gives you access to the npm command.
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ciThis step runs the npm ci shell command to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Cache nextjs build
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: .next/cache
key: ${{ runner.os }}-nextjs-${{ hashFiles('package*.json') }}This step uses the actions/cache action to cache the Next.js build, so that the workflow will attempt to retrieve a cache of the build, and not rebuild it from scratch every time. For more information, see "워크플로 속도를 높이기 위한 종속성 캐싱."
- name: Run build script
run: npm run buildThis step runs the build script.
- name: Run tests
env:
DIFF_FILE: get_diff_files.txt
CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH: src/fixtures/fixtures/changelog-feed.json
run: npm test -- tests/${{ matrix.test-group }}/This step runs the tests using npm test, and the test matrix provides a different value for ${{ matrix.test-group }} for each job in the matrix. It uses the DIFF_FILE environment variable to know which files have changed, and uses the CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH environment variable for the changelog cache file.
# 이렇게 하면 GitHub 리포지토리의 "작업" 탭에 표시되는 워크플로의 이름이 정의됩니다.
name: Node.js Tests
# The `on` keyword lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. You can define multiple events here. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/triggering-a-workflow#using-events-to-trigger-workflows)."
on:
# Add the `workflow_dispatch` event if you want to be able to manually run this workflow. For more information, see [`workflow_dispatch`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#workflow_dispatch).
workflow_dispatch:
# Add the `pull_request` event, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a pull request is created or updated. For more information, see [`pull_request`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#pull_request).
pull_request:
# Add the `push` event with the `branch` filter, so that the workflow runs automatically every time a commit is pushed to a branch called "main". For more information, see [`push`](/actions/using-workflows/events-that-trigger-workflows#push).
push:
branches:
- main
# This modifies the default permissions granted to `GITHUB_TOKEN`. This will vary depending on the needs of your workflow. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/assigning-permissions-to-jobs)."
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: read
# The `concurrency` key ensures that only a single workflow in the same concurrency group will run at the same time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/using-concurrency)."
# `concurrency.group` generates a concurrency group name from the workflow name and pull request information. The `||` operator is used to define fallback values.
# `concurrency.cancel-in-progress` cancels any currently running job or workflow in the same concurrency group.
concurrency:
group: '${{ github.workflow }} @ ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.label || github.head_ref || github.ref }}'
cancel-in-progress: true
# This groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
jobs:
# This defines a job with the ID `test` that is stored within the `jobs` key.
test:
# This configures the job to run on a GitHub-hosted runner or a self-hosted runner, depending on the repository running the workflow.
#
# In this example, the job will run on a self-hosted runner if the repository is named `docs-internal` and is within the `github` organization. If the repository doesn't match this path, then it will run on an `ubuntu-latest` runner hosted by GitHub. For more information on these options, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-jobs/choosing-the-runner-for-a-job)."
runs-on: ${{ fromJSON('["ubuntu-latest", "self-hosted"]')[github.repository == 'github/docs-internal'] }}
# This sets the maximum number of minutes to let the job run before it is automatically canceled. For more information, see [`timeout-minutes`](/actions/using-workflows/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions#jobsjob_idtimeout-minutes).
timeout-minutes: 60
# This section defines the build matrix for your jobs.
strategy:
# Setting `fail-fast` to `false` prevents GitHub from cancelling all in-progress jobs if any matrix job fails.
fail-fast: false
# This creates a matrix named `test-group`, with an array of test groups. These values match the names of test groups that will be run by `npm test`.
matrix:
test-group:
[
content,
graphql,
meta,
rendering,
routing,
unit,
linting,
translations,
]
# This groups together all the steps that will run as part of the `test` job. Each job in a workflow has its own `steps` section.
steps:
# The `uses` keyword tells the job to retrieve the action named `actions/checkout`. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner, allowing you to run actions against your code (such as testing tools). You must use the checkout action any time your workflow will use your repository's code. Some extra options are provided to the action using the `with` key.
- name: Check out repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
lfs: ${{ matrix.test-group == 'content' }}
persist-credentials: 'false'
# This step runs a command to check out large file storage (LFS) objects from the repository.
- name: Checkout LFS objects
run: git lfs checkout
# This step uses the `trilom/file-changes-action` action to gather the files changed in the pull request, so they can be analyzed in the next step. This example is pinned to a specific version of the action, using the `a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b` SHA.
- name: Gather files changed
uses: trilom/file-changes-action@a6ca26c14274c33b15e6499323aac178af06ad4b
id: get_diff_files
with:
output: ' '
# This step runs a shell command that uses an output from the previous step to create a file containing the list of files changed in the pull request.
- name: Insight into changed files
run: |
echo "${{ steps.get_diff_files.outputs.files }}" > get_diff_files.txt
# This step uses the `actions/setup-node` action to install the specified version of the `node` software package on the runner, which gives you access to the `npm` command.
- name: Setup node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 16.14.x
cache: npm
# This step runs the `npm ci` shell command to install the npm software packages for the project.
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
# This step uses the `actions/cache` action to cache the Next.js build, so that the workflow will attempt to retrieve a cache of the build, and not rebuild it from scratch every time. For more information, see "[AUTOTITLE](/actions/using-workflows/caching-dependencies-to-speed-up-workflows)."
- name: Cache nextjs build
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: .next/cache
key: ${{ runner.os }}-nextjs-${{ hashFiles('package*.json') }}
# This step runs the build script.
- name: Run build script
run: npm run build
# This step runs the tests using `npm test`, and the test matrix provides a different value for `${{ matrix.test-group }}` for each job in the matrix. It uses the `DIFF_FILE` environment variable to know which files have changed, and uses the `CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH` environment variable for the changelog cache file.
- name: Run tests
env:
DIFF_FILE: get_diff_files.txt
CHANGELOG_CACHE_FILE_PATH: src/fixtures/fixtures/changelog-feed.json
run: npm test -- tests/${{ matrix.test-group }}/
다음 단계
- GitHub Actions 개념에 대해 알아보려면 “GitHub Actions 이해”를 참조하세요.
- 기본 워크플로를 만들기 위한 단계별 가이드는 "AUTOTITLE"을 참조하세요.
- GitHub Actions의 기본 사항에 익숙한 경우 “워크플로 정보”에서 워크플로 및 해당 기능에 대해 알아볼 수 있습니다.