Note
A project can contain a maximum of 1,200 items and 10,000 archived items. To learn more about automatically archiving items when they meet specific criteria, see Archiving items automatically.
Adding issues and pull requests to a project
You have several options for adding issues and pull requests to your project. You can add them individually, automatically, or in bulk. Furthermore, you can include issues and pull requests from any organization, and you also have the ability to add draft issues that can be converted into regular issues later on. For more information, see Creating draft issues.
Note
Timeline events for Projects is currently in public preview and subject to change.
When you add an issue or pull request to your project, an event will be added to the issue or pull request's timeline. Timeline events will also be added when you remove issues or pull requests and when changes are made to its status field for those items. Timeline events are only visible to people who have at least read permission for the project. If a change is made by a built-in workflow, the activity will be attributed to @github-project-automation.
For more information about making bulk changes to your items after adding them, see Editing items in your project.
Automatically adding issues and pull requests
You can configure a built-in workflow to automatically add issues and pull requests from a repository when they meet specific filter criteria. For more information about configuring a workflow, see Adding items automatically.
Pasting the URL of an issue or pull request
You can copy the URL of an issue or pull request into your clipboard and paste that into your project.
-
Place your cursor in the bottom row of the project, next to the .
-
Paste the URL of the issue or pull request.
-
To add the issue or pull request, press Return.
Searching for an issue or pull request
If you know the issue or pull request number or if you know part of the title, you can search for an issue or pull request directly from your project.
-
Place your cursor in the bottom row of the project, next to the .

-
To open the list of repositories, type #.
-
Select the repository where the pull request or issue is located. You can type part of the repository name to narrow down your options.
-
Select the issue or pull request. You can type part of the title to narrow down your options.
Bulk adding issues and pull requests
You can add multiple issues and pull requests from your project and use filters, such as label:bug, to narrow down your search.
-
In the bottom row of the project, click .
-
Click Add item from repository.
-
Optionally, to change the repository, click the dropdown and select a repository. You can also search for specific issues and pull requests.
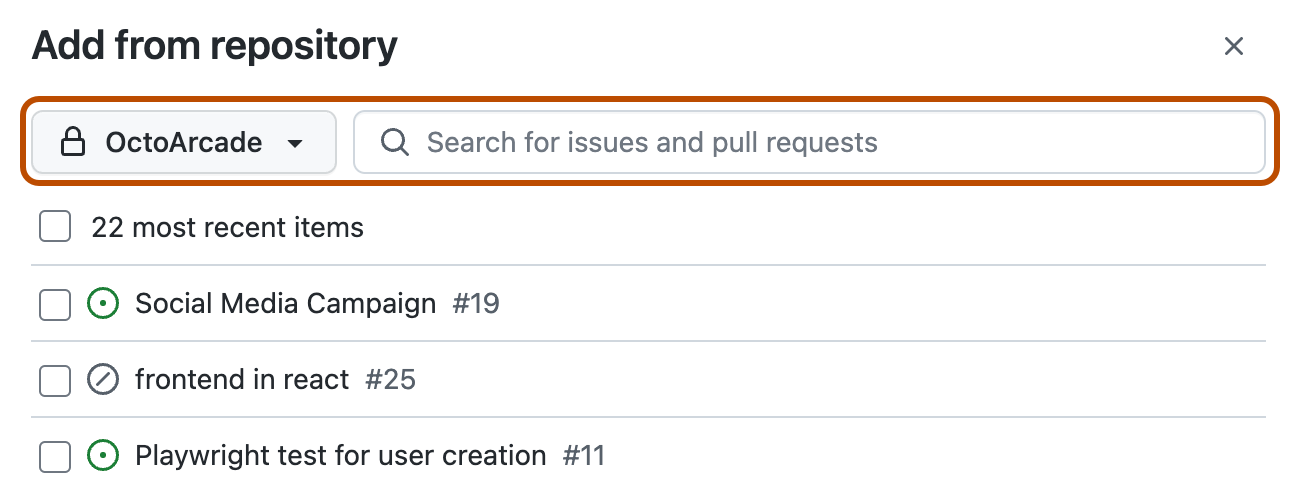
-
Select the issues and pull requests you want to add.
-
Click Add selected items.
Adding multiple issues or pull requests from a repository
You can also add issues and pull requests to your project from a repository's issue and pull request lists.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the repository that contains the issues or pull requests you want to add to your project.
-
Under your repository name, click Issues or Pull requests.

-
Select the issues or pull requests you want to add to your project.
-
To select individual issues or pull requests, to the left of the title of each issue or pull request you want to add to your project, select the checkbox.
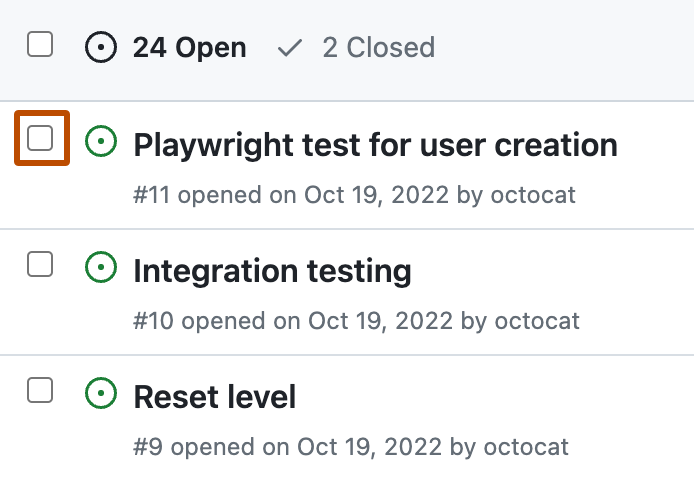
-
To select every issue or pull request on the page, at the top of the list of issues or pull requests, select all.
-
-
Above the list of issues or pull requests, click Projects.
-
Click the projects you want to add the selected issues or pull requests to.
Assigning a project from within an issue or pull request
You can also add an issue or pull request to your project from within the issue or pull request itself.
- Navigate to the issue or pull request that you want to add to a project.
- In the side bar, click Projects.
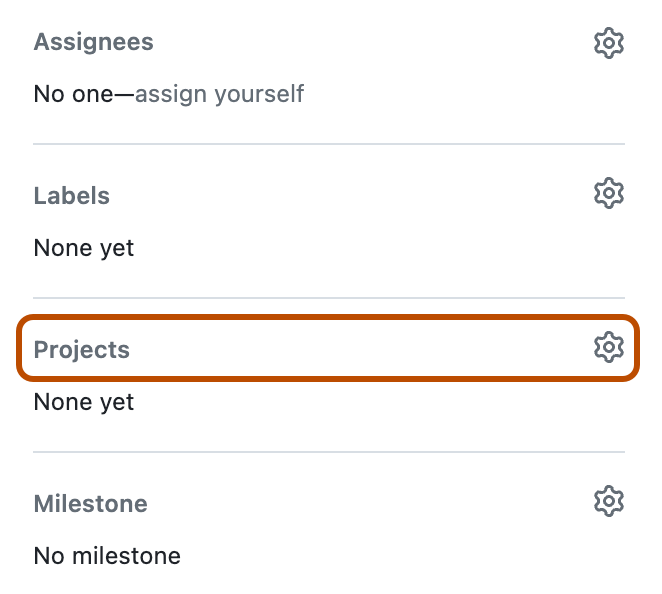
- Select the project that you want to add the issue or pull request to.
- Optionally, populate the custom fields.
Using the command palette to add an issue or pull request
You can use the command palette when viewing your project to quickly add items.
-
To open the project command palette, press Command+K (Mac) or Ctrl+K (Windows/Linux).
-
Start typing "Add items" and press Return.
-
Optionally, to change the repository, click the dropdown and select a repository. You can also search for specific issues and pull requests.

-
Select the issues and pull requests you want to add.
-
Click Add selected items.
Creating issues
You can quickly create issues without leaving your project. When using a view that is grouped by a field, creating an issue in that group will automatically set the new issue's field to the group's value. For example, if you group your view by "Status", when you create an issue in the "Todo" group, the new issue's "Status" will automatically be set to "Todo."
-
At the bottom of a table, group of items, or a column in board layout, click .

-
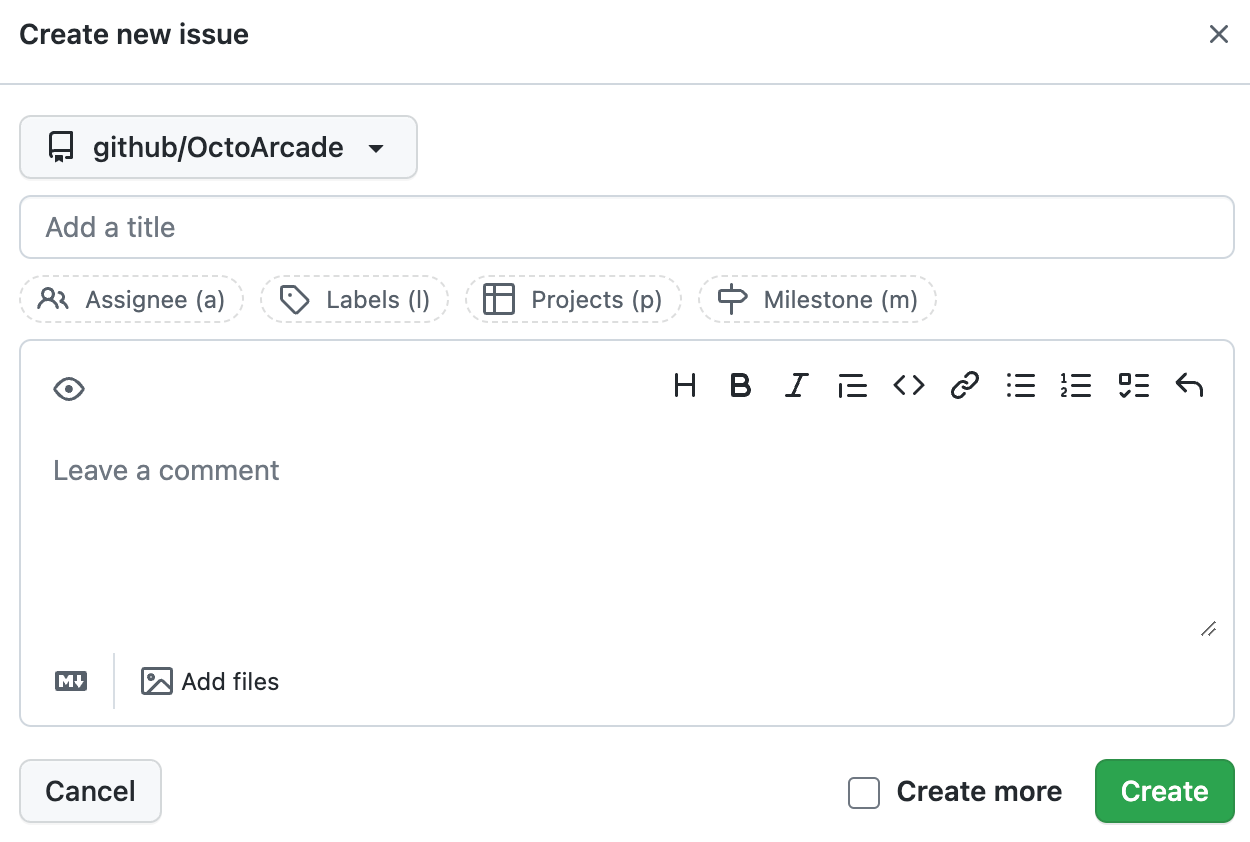
Click Create new issue.
-
At the top of the "Create new issue" dialog, select the repository where you want the new issue to be created.
-
Below the repository dropdown, type a title for the new issue.
-
Optionally, use the fields below the title field to set assignees, labels, and milestones, and add the new issue to other projects.
-
Optionally, type a description for your issue.
-
Optionally, if you want to create more issues, select Create more and the dialog will reopen when you create your issue.
-
Click Create.
Creating draft issues
Draft issues are useful to quickly capture ideas. Unlike issues and pull requests that are referenced from your repositories, draft issues exist only in your project.
-
Place your cursor in the bottom row of the project, next to the .

-
Type your idea, then press Enter.
-
To add body text, click on the title of the draft issue. In the markdown input box that appears, enter the text for the draft issue body, then click Save.
Draft issues can have a title, text body, assignees, and any custom fields from your project. In order to populate the repository, labels, or milestones for a draft issue, you must first convert the draft issue to an issue. For more information, see Converting draft issues to issues.
Note
Users will not receive notifications when they are assigned to or mentioned in a draft issue unless the draft issue is converted to an issue.