Note
Your site administrator must set up Dependabot updates for your GitHub Enterprise Server instance before you can use this feature. For more information, see Enabling Dependabot for your enterprise.
You may not be able to enable or disable Dependabot updates if an enterprise owner has set a policy at the enterprise level. For more information, see Enforcing policies for code security and analysis for your enterprise.
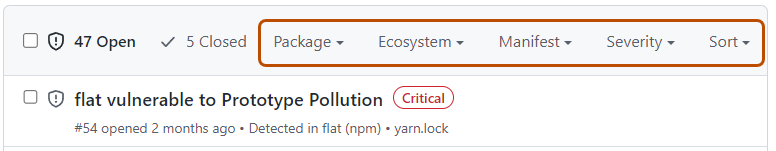
Your repository's Dependabot alerts tab lists all open and closed Dependabot alerts and corresponding Dependabot security updates. You can filter alerts by package, ecosystem, or manifest. You can sort the list of alerts, and you can click into specific alerts for more details. You can also dismiss or reopen alerts, either one by one or by selecting multiple alerts at once. For more information, see About Dependabot alerts.
You can enable automatic security updates for any repository that uses Dependabot alerts and the dependency graph. For more information, see About Dependabot security updates.
About updates for vulnerable dependencies in your repository
GitHub Enterprise Server generates Dependabot alerts when we detect that the default branch of your codebase is using dependencies with known security risks. For repositories where Dependabot security updates are enabled, when GitHub Enterprise Server detects a vulnerable dependency in the default branch, Dependabot creates a pull request to fix it. The pull request will upgrade the dependency to the minimum possible secure version needed to avoid the vulnerability.
Dependabot doesn't generate Dependabot alerts for malware. For more information, see About the GitHub Advisory database.
Each Dependabot alert has a unique numeric identifier and the Dependabot alerts tab lists an alert for every detected vulnerability. Legacy Dependabot alerts grouped vulnerabilities by dependency and generated a single alert per dependency. If you navigate to a legacy Dependabot alert, you will be redirected to a Dependabot alerts tab filtered for that package.
You can filter and sort Dependabot alerts using a variety of filters and sort options available on the user interface. For more information, see Prioritizing Dependabot alerts below.
You can also audit actions taken in response to Dependabot alerts. For more information, see Auditing security alerts.
Prioritizing Dependabot alerts
GitHub helps you prioritize fixing Dependabot alerts. By default, Dependabot alerts are sorted by importance. The "Most important" sort order helps you prioritize which Dependabot alerts to focus on first. Alerts are ranked based on their potential impact, actionability, and relevance. Our prioritization calculation is constantly being improved and includes factors like CVSS score, dependency scope, and whether vulnerable function calls are found for the alert.
You can also use Dependabot auto-triage rules to prioritize Dependabot alerts. For more information, see “About Dependabot auto-triage rules.”
You can sort and filter Dependabot alerts by typing filters as key:value pairs into the search bar.
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
ecosystem | Displays alerts for the selected ecosystem | Use ecosystem:npm to show Dependabot alerts for npm |
has | Displays alerts meeting the selected filter criteria | Use has:patch to show alerts related to advisories that have a patch |
is | Displays alerts based on their state | Use is:open to show open alerts |
manifest | Displays alerts for the selected manifest | Use manifest:webwolf/pom.xml to show alerts on the pom.xml file of the webwolf application |
package | Displays alerts for the selected package | Use package:django to show alerts for django |
resolution | Displays alerts of the selected resolution status | Use resolution:no-bandwidth to show alerts previously parked due to lack of resources or time to fix them |
repo | Displays alerts based on the repository they relate to Note that this filter is only available for security overview. For more information, see About security overview | Use repo:octocat-repo to show alerts in the repository called octocat-repo |
scope | Displays alerts based on the scope of the dependency they relate to | Use scope:development to show alerts for dependencies that are only used during development |
severity | Displays alerts based on their level of severity | Use severity:high to show alerts with a severity of High |
sort | Displays alerts according to the selected sort order | The default sorting option for alerts is sort:most-important, which ranks alerts by importanceUse sort:newest to show the latest alerts reported by Dependabot |
In addition to the filters available via the search bar, you can sort and filter Dependabot alerts using the dropdown menus at the top of the alert list. Alternatively, to filter by label, click a label assigned to an alert to automatically apply that filter to the alert list.
The search bar also allows for full text searching of alerts and related security advisories. You can search for part of a security advisory name or description to return the alerts in your repository that relate to that security advisory. For example, searching for yaml.load() API could execute arbitrary code will return Dependabot alerts linked to PyYAML insecurely deserializes YAML strings leading to arbitrary code execution as the search string appears in the advisory description.
Supported ecosystems and manifests for dependency scope
The table below summarizes whether dependency scope is supported for various ecosystems and manifests, that is, whether Dependabot can identify if a dependency is used for development or production.
| Language | Ecosystem | Manifest file | Dependency scope supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dart | pub | pubspec.yaml | |
| Dart | pub | pubspec.lock | |
| Go | Go modules | go.mod | No, defaults to runtime |
| Java | Maven | pom.xml | test maps to development, else scope defaults to runtime |
| JavaScript | npm | package.json | |
| JavaScript | npm | package-lock.json | |
| JavaScript | npm | pnpm-lock.yaml | |
| JavaScript | yarn v1 | yarn.lock | No, defaults to runtime |
| PHP | Composer | composer.json | |
| PHP | Composer | composer.lock | |
| Python | Poetry | poetry.lock | |
| Python | Poetry | pyproject.toml | |
| Python | pip | requirements.txt | Scope is development if the filename contains test or dev, else it is runtime |
| Python | pip | pipfile.lock | |
| Python | pip | pipfile | |
| Ruby | RubyGems | Gemfile | |
| Ruby | RubyGems | Gemfile.lock | No, defaults to runtime |
| Rust | Cargo | Cargo.toml | |
| Rust | Cargo | Cargo.lock | No, defaults to runtime |
| YAML | GitHub Actions | - | No, defaults to runtime |
| .NET (C#, F#, VB, etc.) | NuGet | .csproj / .vbproj .vcxproj / .fsproj | No, defaults to runtime |
| .NET | NuGet | packages.config | No, defaults to runtime |
| .NET | NuGet | .nuspec | When the tag != runtime |
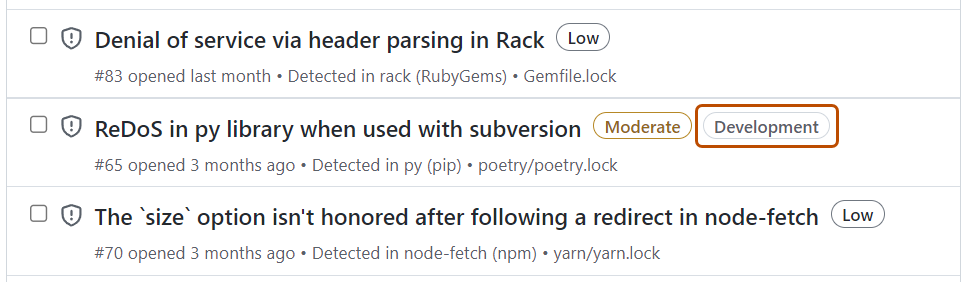
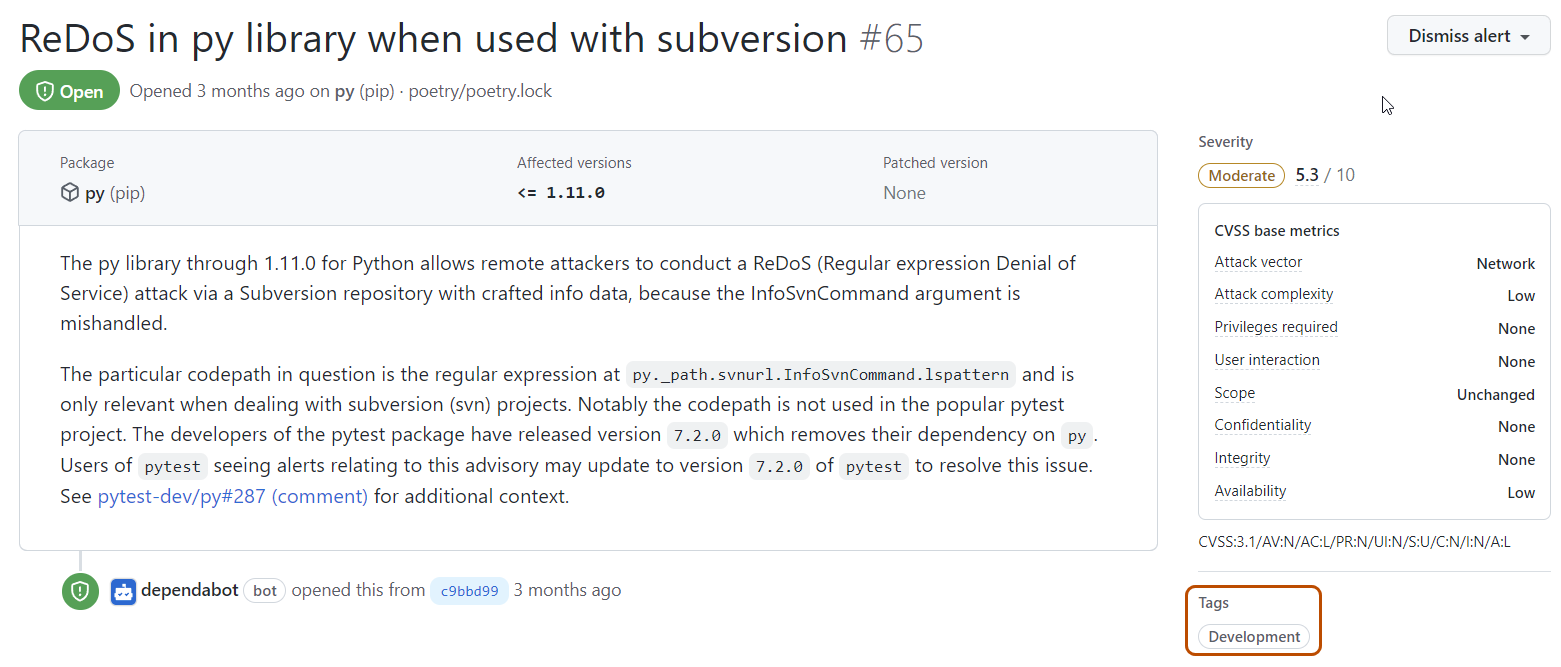
Alerts for packages listed as development dependencies are marked with the Development label on the Dependabot alerts page and are also available for filtering via the scope filter.
The alert details page of alerts on development-scoped packages shows a "Tags" section containing a Development label.
Viewing Dependabot alerts
You can view all open and closed Dependabot alerts and corresponding Dependabot security updates in your repository's Dependabot alerts tab. You can sort and filter Dependabot alerts by selecting a filter from the dropdown menu.
To view summaries of alerts for all or a subset of repositories owned by your organization, use security overview. For more information, see About security overview.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under the repository name, click Security. If you cannot see the "Security" tab, select the dropdown menu, and then click Security.
-
In the "Vulnerability alerts" sidebar of security overview, click Dependabot. If this option is missing, it means you don't have access to security alerts and need to be given access. For more information, see Managing security and analysis settings for your repository.
-
Optionally, to filter alerts, select a filter in a dropdown menu then click the filter that you would like to apply. You can also type filters into the search bar. Alternatively, to filter by label, click a label assigned to an alert to automatically apply that filter to the alert list. For more information about filtering and sorting alerts, see Prioritizing Dependabot alerts.

-
Click the alert that you would like to view.
-
Optionally, to suggest an improvement to the related security advisory, on the right-hand side of the alert details page, click Suggest improvements for this advisory on the GitHub Advisory Database. For more information, see Editing security advisories in the GitHub Advisory Database.
Reviewing and fixing alerts
It’s important to ensure that all of your dependencies are clean of any security weaknesses. When Dependabot discovers vulnerabilities in your dependencies, you should assess your project’s level of exposure and determine what remediation steps to take to secure your application.
If a patched version of the dependency is available, you can generate a Dependabot pull request to update this dependency directly from a Dependabot alert. If you have Dependabot security updates enabled, the pull request may be linked in the Dependabot alert.
In cases where a patched version is not available, or you can’t update to the secure version, Dependabot shares additional information to help you determine next steps. When you click through to view a Dependabot alert, you can see the full details of the security advisory for the dependency including the affected functions. You can then check whether your code calls the impacted functions. This information can help you further assess your risk level, and determine workarounds or if you’re able to accept the risk represented by the security advisory.
Fixing vulnerable dependencies
-
View the details for an alert. For more information, see Viewing Dependabot alerts (above).
-
If you have Dependabot security updates enabled, there may be a link to a pull request that will fix the dependency. Alternatively, you can click Create Dependabot security update at the top of the alert details page to create a pull request.
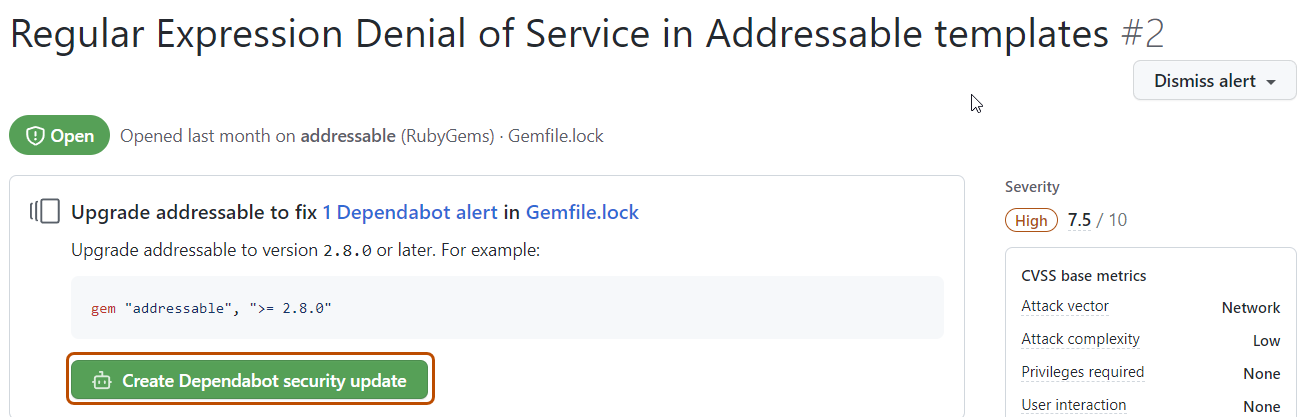
-
Optionally, if you do not use Dependabot security updates, you can use the information on the page to decide which version of the dependency to upgrade to and create a pull request to update the dependency to a secure version.
-
When you're ready to update your dependency and resolve the vulnerability, merge the pull request.
Each pull request raised by Dependabot includes information on commands you can use to control Dependabot. For more information, see Managing pull requests for dependency updates.
Dismissing Dependabot alerts
Note
You can only dismiss open alerts.
If you schedule extensive work to upgrade a dependency, or decide that an alert does not need to be fixed, you can dismiss the alert. Dismissing alerts that you have already assessed makes it easier to triage new alerts as they appear.
-
View the details for an alert. For more information, see Viewing vulnerable dependencies (above).
-
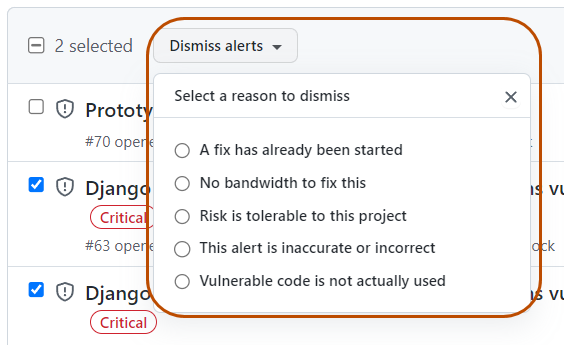
Select the "Dismiss" dropdown, and click a reason for dismissing the alert. Unfixed dismissed alerts can be reopened later.
-
Optionally, add a dismissal comment. The dismissal comment will be added to the alert timeline and can be used as justification during auditing and reporting. You can retrieve or set a comment by using the GraphQL API. The comment is contained in the
dismissCommentfield. For more information, see Objects in the GraphQL API documentation.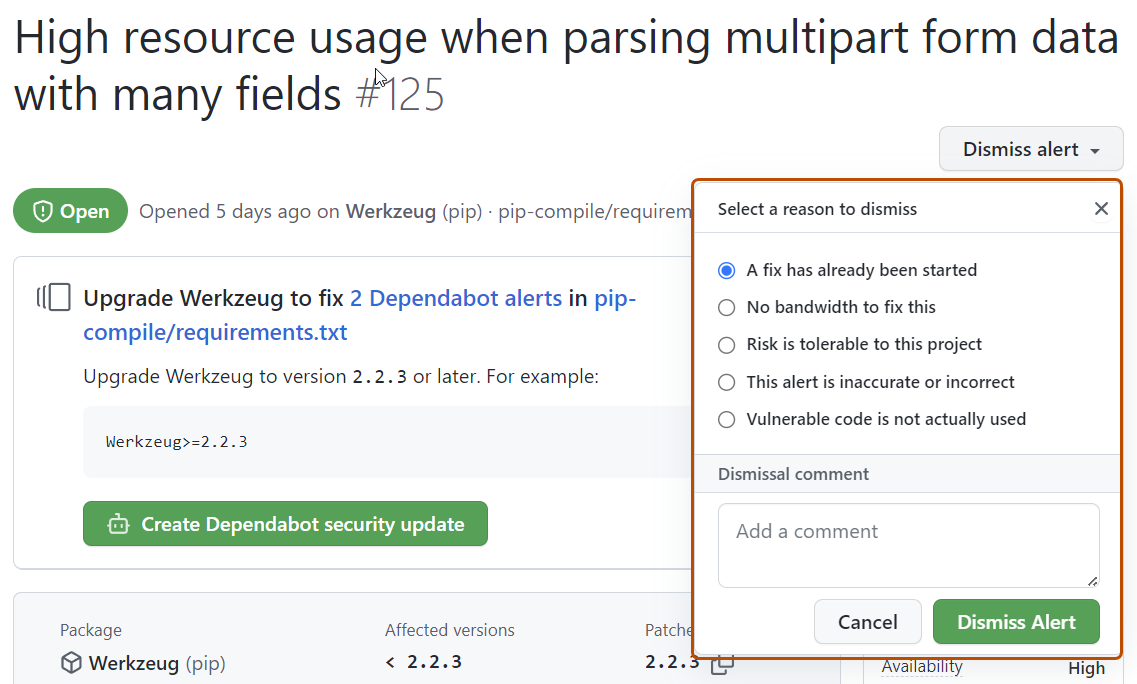
-
Click Dismiss alert.
Dismissing multiple alerts at once
- View the open Dependabot alerts. For more information, see Viewing and updating Dependabot alerts.
- Optionally, filter the list of alerts by selecting a dropdown menu, then clicking the filter that you would like to apply. You can also type filters into the search bar.
- To the left of each alert title, select the alerts that you want to dismiss.
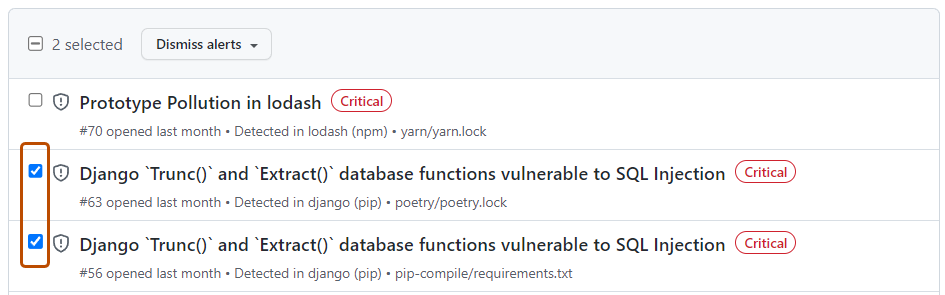
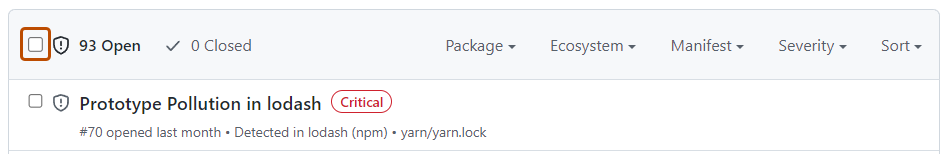
- Optionally, at the top of the list of alerts, select all alerts on the page.
- Select the "Dismiss alerts" dropdown, and click a reason for dismissing the alerts.
Viewing and updating closed alerts
You can view all open alerts, and you can reopen alerts that have been previously dismissed. Closed alerts that have already been fixed cannot be reopened.
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
-
Under the repository name, click Security. If you cannot see the "Security" tab, select the dropdown menu, and then click Security.

-
In the "Vulnerability alerts" sidebar of security overview, click Dependabot. If this option is missing, it means you don't have access to security alerts and need to be given access. For more information, see Managing security and analysis settings for your repository.

-
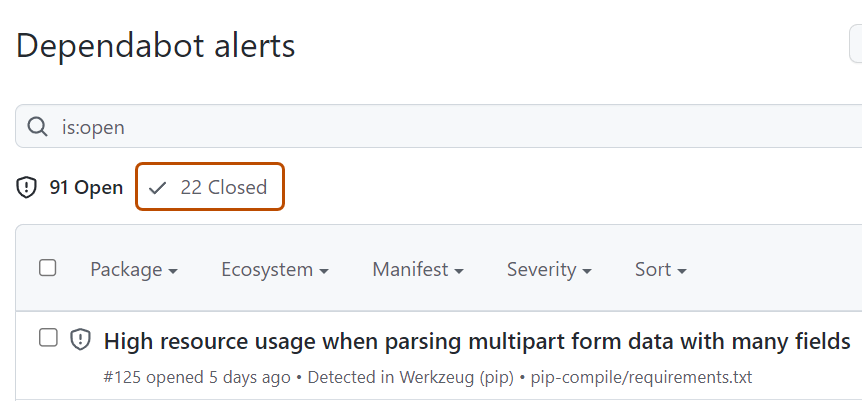
To just view closed alerts, click Closed.
-
Click the alert that you would like to view or update.
-
Optionally, if the alert was dismissed and you wish to reopen it, click Reopen. Alerts that have already been fixed cannot be reopened.

Reopening multiple alerts at once
- View the closed Dependabot alerts. For more information, see Viewing and updating Dependabot alerts (above).
- To the left of each alert title, select the alerts that you want to reopen by clicking the checkbox adjacent to each alert.
- Optionally, at the top of the list of alerts, select all closed alerts on the page.
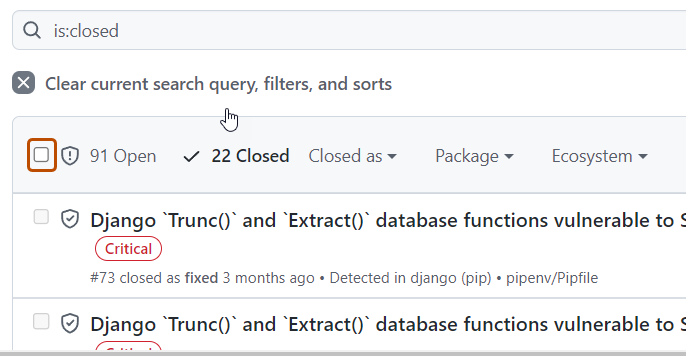
- Click Reopen to reopen the alerts. Alerts that have already been fixed cannot be reopened.
Reviewing the audit logs for Dependabot alerts
When a member of your organization or enterprise performs an action related to Dependabot alerts, you can review the actions in the audit log. For more information about accessing the log, see Reviewing the audit log for your organization and Accessing the audit log for your enterprise.
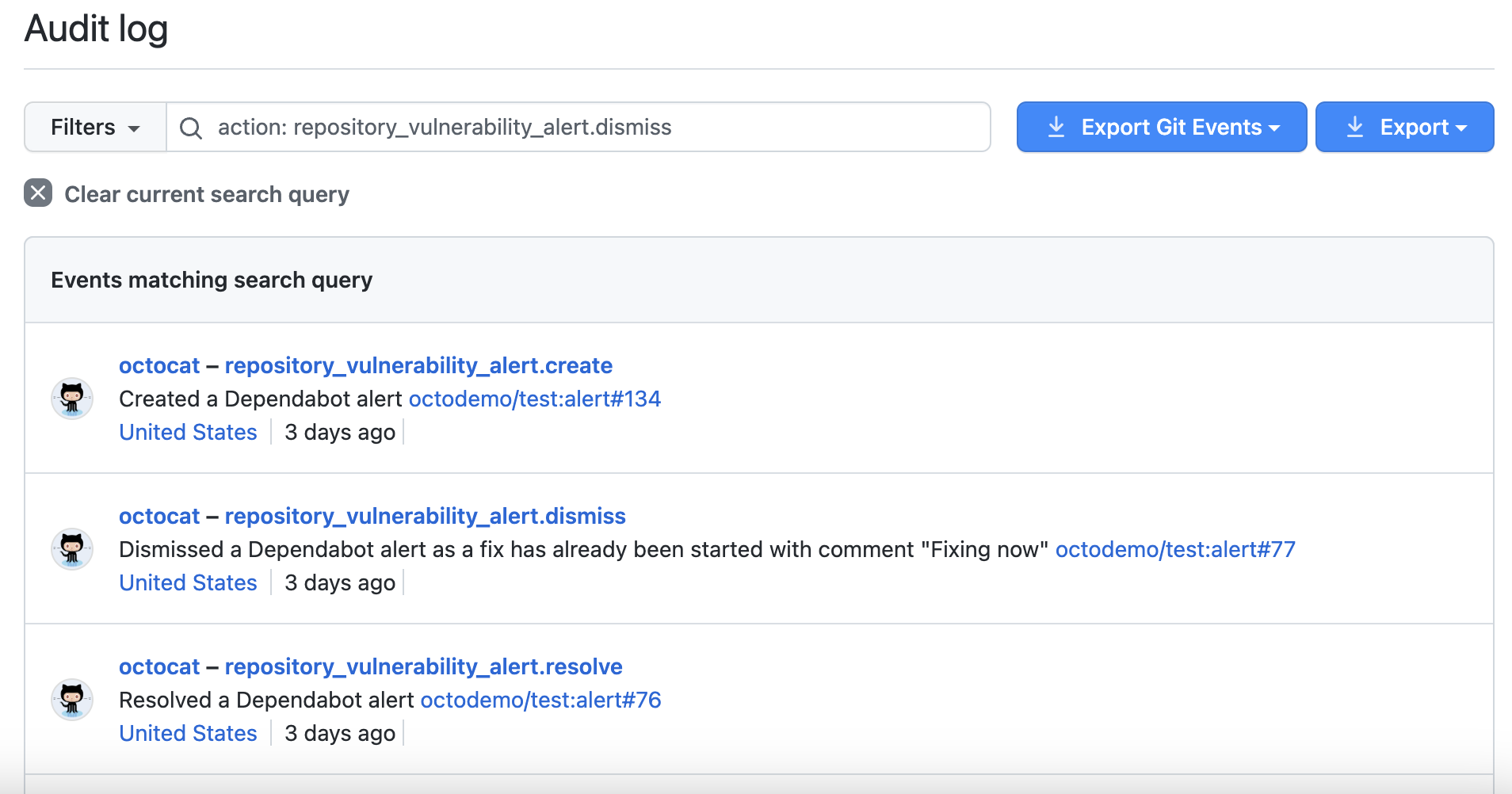
Events in your audit log for Dependabot alerts include details such as who performed the action, what the action was, and when the action was performed. The event also includes a link to the alert itself. When a member of your organization dismisses an alert, the event displays the dismissal reason and comment. For information on the Dependabot alerts actions, see the repository_vulnerability_alert category in Audit log events for your organization and Audit log events for your enterprise.